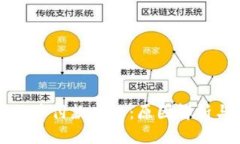
引言
随着区块链技术的不断发展,以太坊作为一个强大的去中心化平台,越来越多地被用于智能合约和数字资产的管理。而将整数(int)数据存储到以太坊钱包中,虽然不是最常见的做法,但在某些特定的应用场景中却是非常重要的。在这篇文章中,我们将深入探讨如何将整数数据放到以太坊钱包中,包括相关的技术细节、智能合约的编写以及使用钱包的具体步骤。
一、以太坊钱包简介

以太坊钱包是一种用于管理以太坊资产以及与以太坊网络交互的工具。用户通过钱包可以发送和接收以太坊(ETH)和其他代币,同时可以与智能合约进行交互。以太坊钱包类型五花八门,包括软件钱包、硬件钱包和在线钱包等,其中每种都有其独特的优势和适用场景。
二、智能合约与数据存储
在以太坊上,数据的存储主要依靠智能合约。智能合约是以太坊网络中执行的一段代码,它可以存储状态变量并在满足特定条件时执行特定操作。为了将整数数据存储到以太坊钱包中,我们需要使用智能合约进行操作。以下是一些基本步骤:
1. 编写智能合约
在编写智能合约之前,我们首先需要了解Solidity,这是一种为以太坊平台设计的编程语言。一个简单的智能合约可以用来存储和检索整数数据。下面是一个示例合约:
```solidity pragma solidity ^0.8.0; contract IntegerStorage { uint256 storedInteger; function setInteger(uint256 _integer) public { storedInteger = _integer; } function getInteger() public view returns (uint256) { return storedInteger; } } ```在上述合约中,`storedInteger`变量被设置为公有状态变量,允许用户通过`setInteger`函数设置值,并通过`getInteger`函数获取值。
2. 部署智能合约
编写完智能合约后,我们需要将其部署到以太坊网络。这通常可以通过如Remix、Truffle等工具进行,步骤如下:
- 在Remix中创建新的.sol文件,并粘贴合约代码。
- 选择编译插件并编译合约。
- 在部署插件中选择合理的网络(如Ganache或主网),并点击部署。
3. 与智能合约交互
合约部署后,我们可以通过钱包与合约进行交互。用户可以通过钱包发送交易来调用`setInteger`函数,将整数值存储在以太坊网络上。在发送交易时,需要指定合约地址和调用的函数。
总结
总结来说,将整数数据存储到以太坊钱包主要依赖于智能合约的开发和部署。在此过程中,我们需要了解Solidity语言和智能合约的基本操作,以及如何与以太坊钱包连接。
常见问题解答
如何选择合适的以太坊钱包?
在选择以太坊钱包时,用户需要考虑多个因素,包括安全性、易用性和功能性。硬件钱包如Ledger和Trezor提供最高水平的安全性,适合长期存储数字资产。而软件钱包如MetaMask则更加灵活,方便与DApp进行交互。
以太坊钱包的安全性如何提高?
要提高以太坊钱包的安全性,用户可以采取以下几种措施:
- 为钱包设置强密码,并定期更新。
- 启用双重身份验证(2FA)。
- 使用硬件钱包存储大量资产。
- 谨慎对待钓鱼网站和假冒应用。
智能合约的常见漏洞有哪些?
智能合约的常见漏洞主要包括重入攻击、整数溢出、不可预测性以及访问控制不足等。在开发合约时,开发者应仔细审查代码,并使用静态分析工具检查潜在问题。
部署智能合约需要多少费用?
部署智能合约需要支付网络交易费用,称为“Gas”。Gas的价格波动较大,用户可以根据网络的拥堵程度调整Gas价格。在合约部署前,建议查看当前Gas价格,以便更好地估算费用。
结论
在以太坊网络上存储整数数据虽然看似简单,但其背后却蕴含着丰富的技术知识和开发技能。通过学习智能合约的开发和钱包的使用,用户不仅能更好地进行数字资产的管理,还能为自我学习和实践打开更广阔的视野。